Ways of exchanging video surveillance data
Video surveillance data is commonly exchanged between systems in one of two ways: unicast or multicast. Learn which way of exchanging video surveillance data is right for you.

Video surveillance data is commonly exchanged between systems using one of two methods: unicast or multicast. Understanding the differences between these video transmission methods can help you optimize bandwidth usage, reduce network strain, and ensure a smooth video streaming experience.
In this blog post, we'll explain how video surveillance data is transmitted, the pros and cons of unicast and multicast, and how to choose the right method for your system.
CHECKLIST
What is video surveillance data transmission?
Video surveillance systems capture and share real-time video feeds over a network. This data can come from a variety of sources, including:
-
Security cameras
-
Intercom systems
-
Door sensors
-
Other connected devices
With advances in AI-powered image processing and high-speed internet, video surveillance is no longer just for security. Insights from video data are valuable to multiple departments, including operations, marketing, and executive teams.
However, sharing large volumes of video data can put significant strain on your network. Choosing the right transmission method is crucial to maintaining performance and video quality.
BLOG
Unicast vs. multicast: key differences
What is unicast transmission?
Unicast is a one-to-one communication method. Each time a user requests a video stream, the system creates a unique copy of the stream for that user.
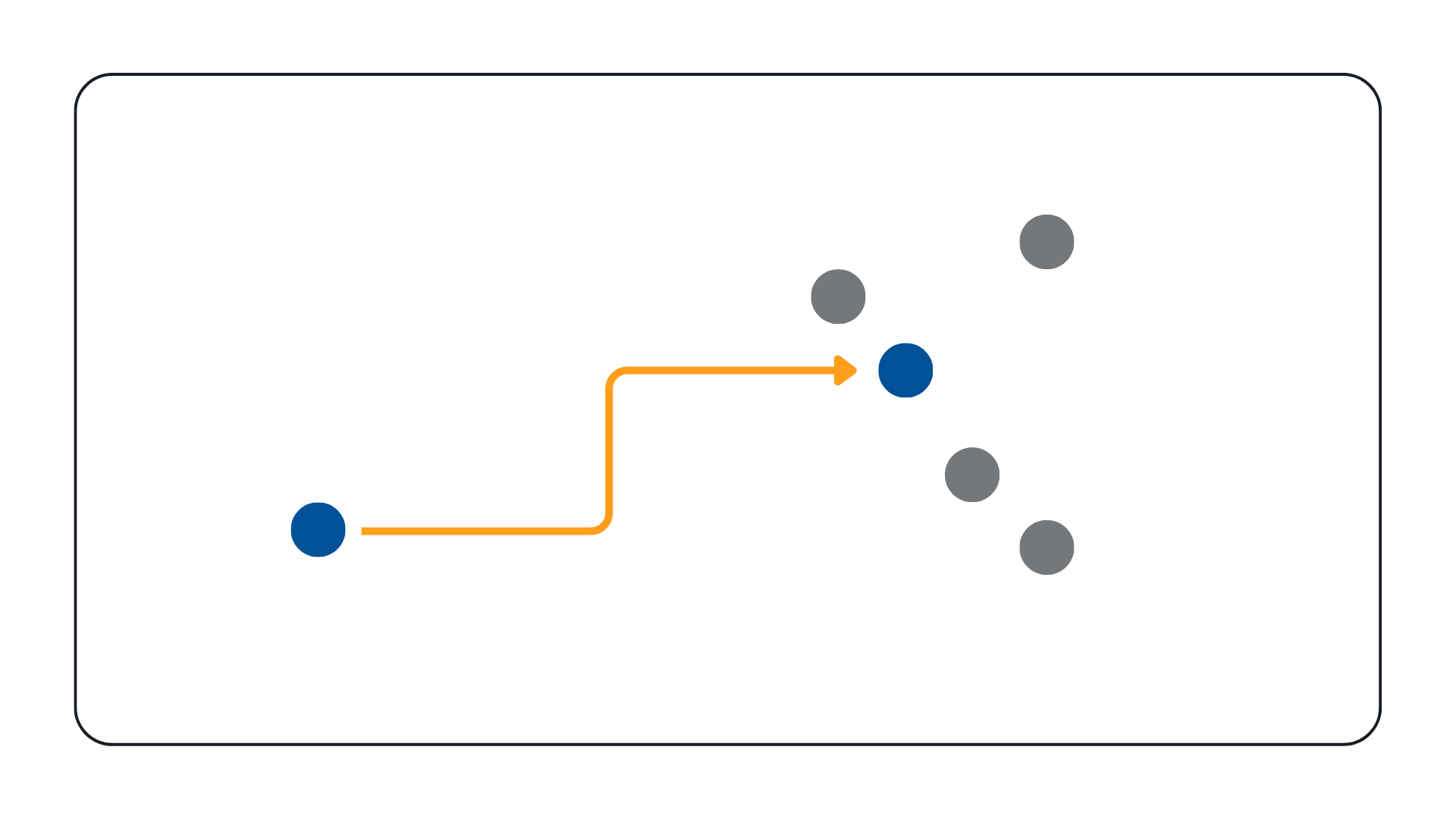
Example: If three operators want to view the same camera feed, unicast sends three separate video streams, each consuming network bandwidth.
Pros of unicast:
-
Easier to set up and configure
-
Compatible with most cameras and networks
Cons of unicast:
-
Higher bandwidth usage
-
Can overload the network with multiple viewers
What is multicast transmission?
Multicast is a one-to-many communication method. The camera sends a single stream to the network switch, which replicates and delivers it to multiple users.
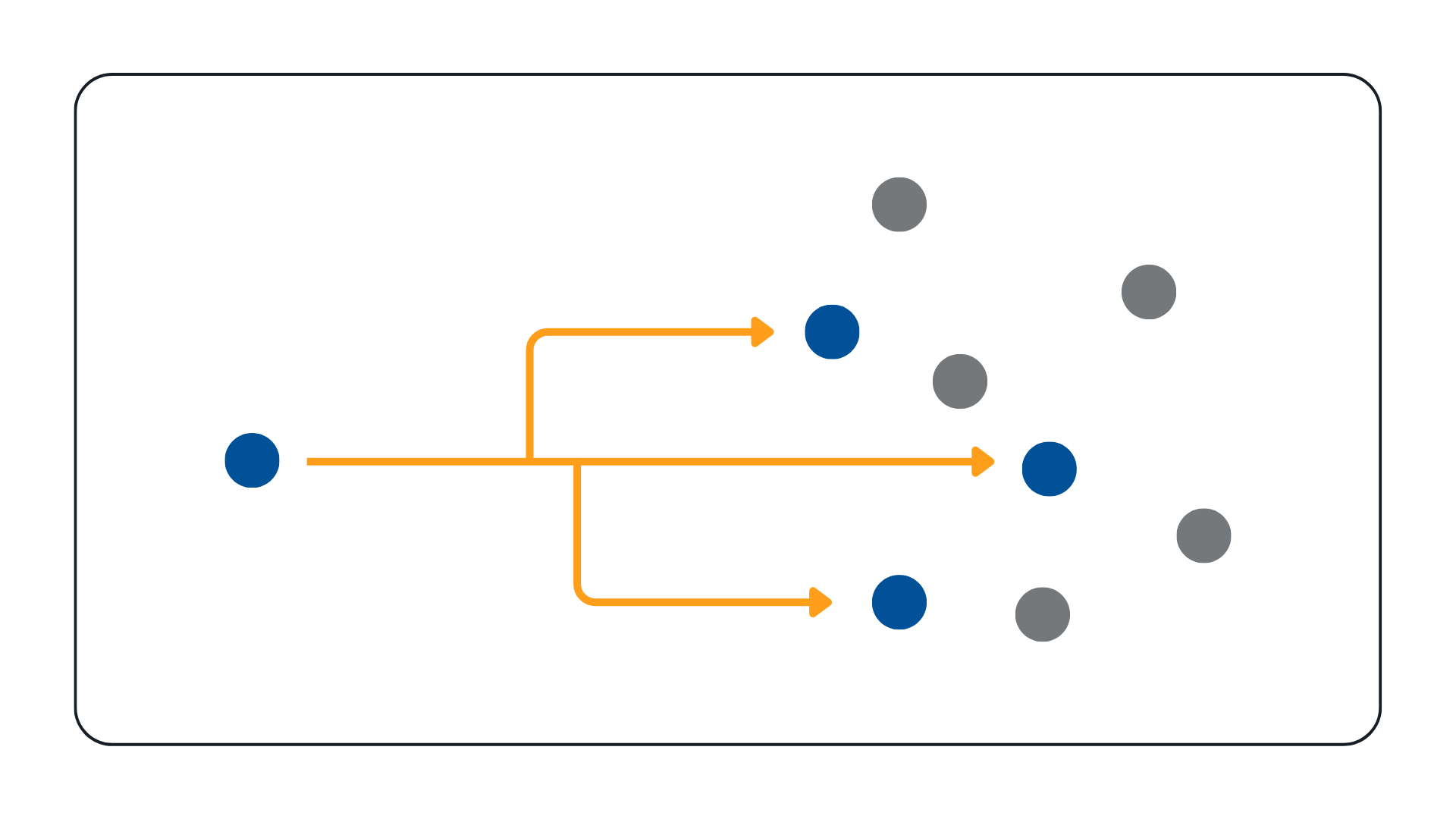
Example: If three operators view the same feed, multicast sends one video stream, reducing bandwidth consumption.
Pros of multicast:
-
More efficient for multiple viewers
-
Reduces network congestion
Cons of multicast:
-
Requires multicast-enabled hardware (routers, switches)
-
More complex to configure
What about broadcast transmission?
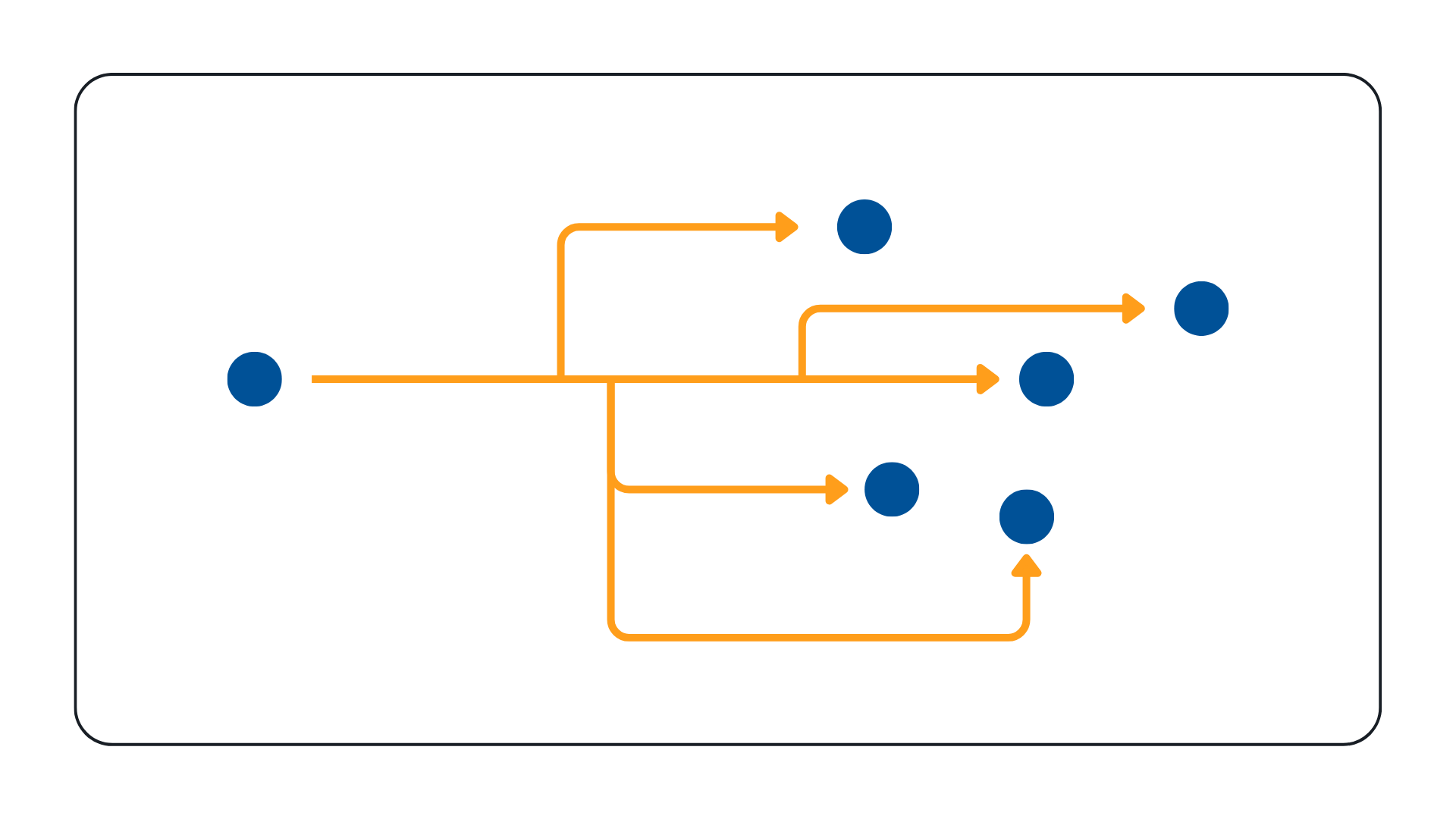
Broadcast is a one-to-all transmission method, where video data is sent to all devices on the network. Because it uses excessive bandwidth, it's not recommended for video surveillance.
Which data transmission method is right for you?
When deciding between unicast and multicast, consider the following factors:
1. Network capacity
-
Smaller networks or systems with few viewers may perform well with unicast.
-
Larger networks or systems with many viewers benefit from multicast to minimize bandwidth use.
2. Hardware compatibility
-
Unicast requires cameras that support concurrent connections.
-
Multicast requires specialized routers and switches for packet replication.
3. Scalability needs
-
If you anticipate growth or need to accommodate remote viewers, a hybrid approach using both methods may be best.
Get the best of both worlds with a VMS that adapts
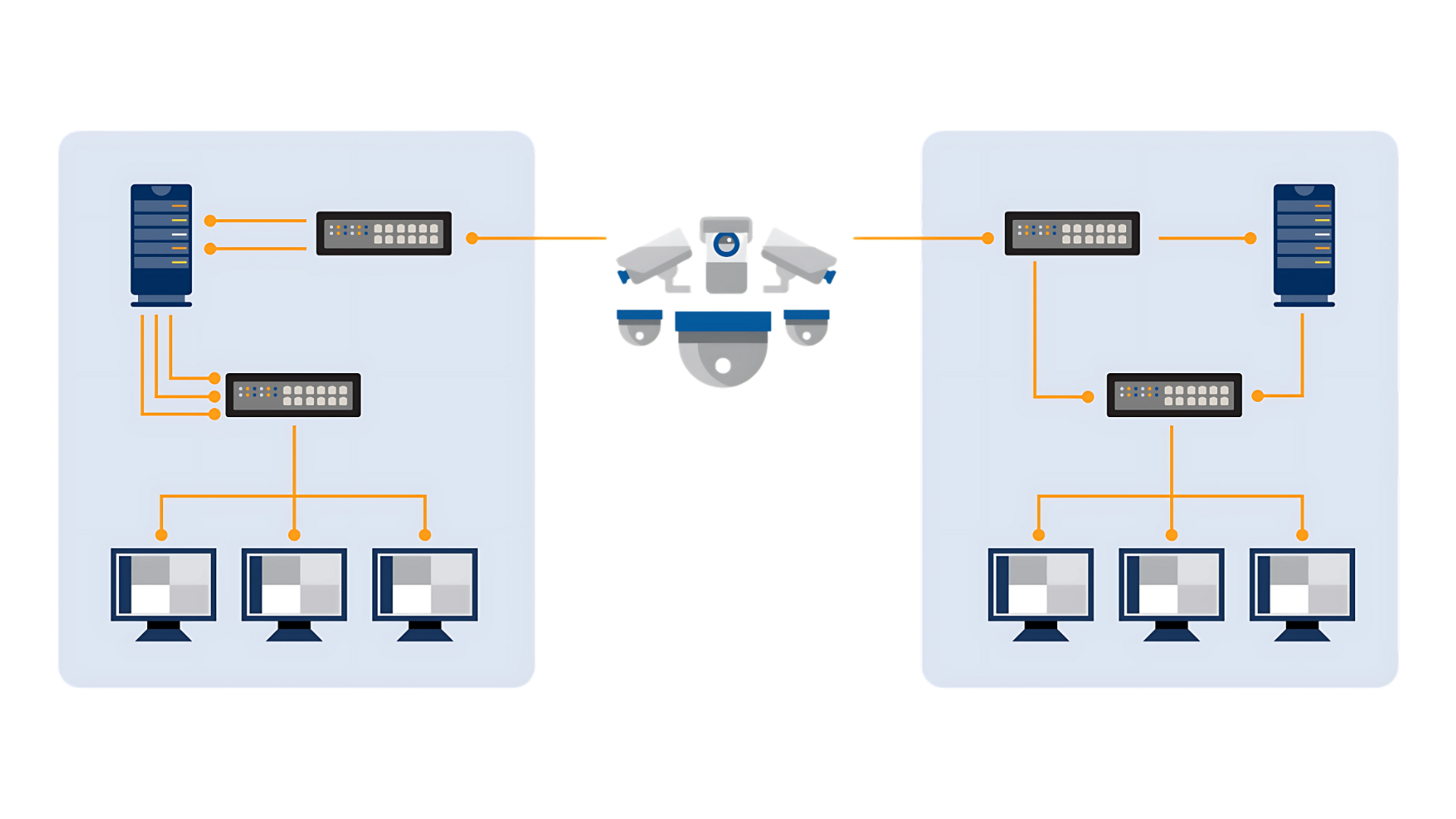
In many cases, a modern video management system (VMS) can intelligently switch between unicast and multicast to optimize performance.
Genetec Security Center Omnicast™ is designed to handle diverse network environments by:
- Automatically switching between unicast and multicast as needed
- Transforming unicast cameras into multicast for local users
- Providing unicast streams to remote viewers without overloading the network
Whether your team is on-site or working remotely, Omnicast ensures you get the best video quality with minimal network strain.
FEATURE NOTE
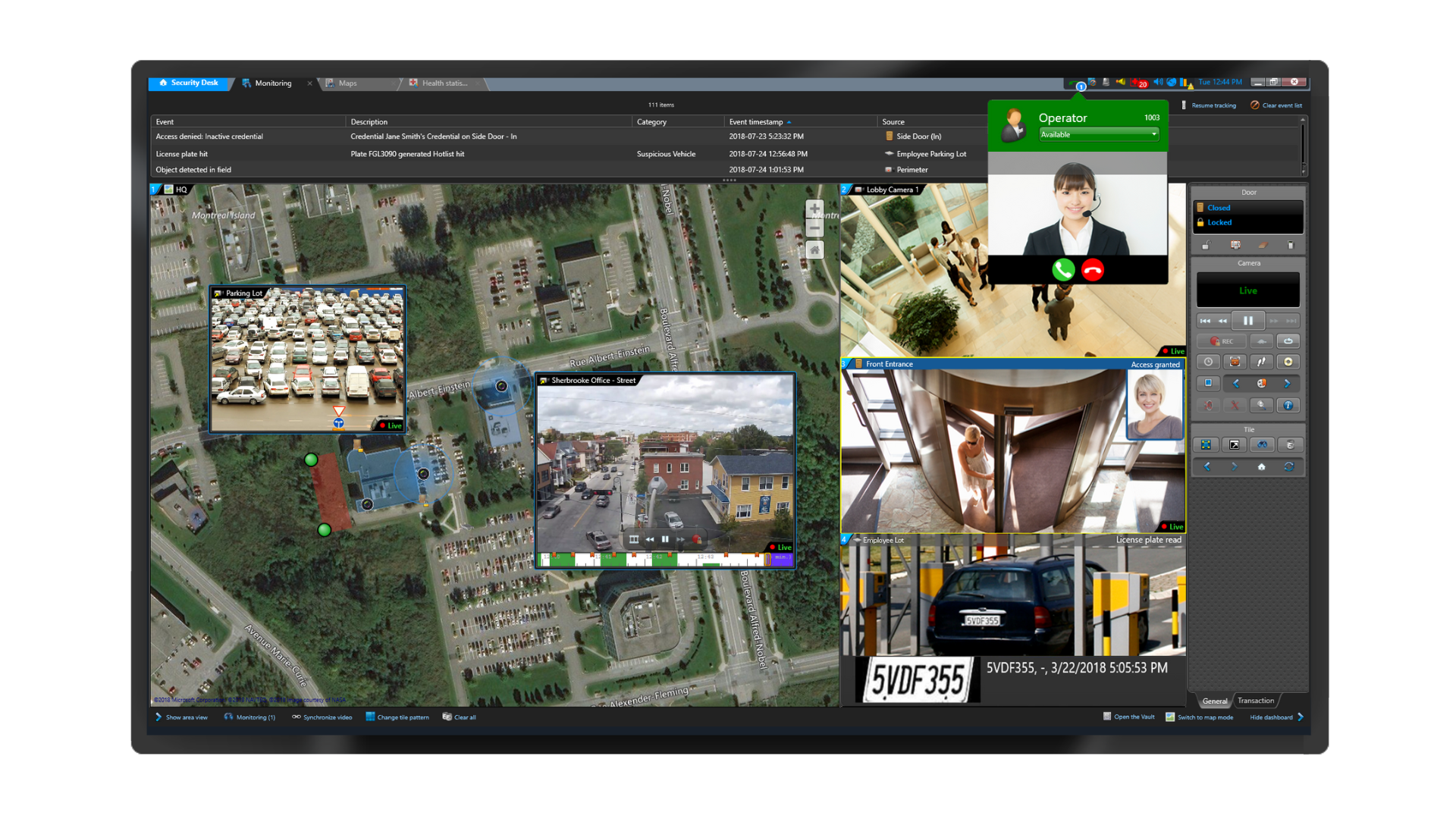
The best part is that all of your data is pulled into Genetec Security Center, which provides a unified view of all your security systems.
With a unified physical security platform, you can:
- Monitor and manage all video feeds
- Access real-time data from maps and dashboards
- Improve response times during security incidents
